
Medically reviewed by Dr. Tan Chuan Chien, Consultant General Surgeon (Breast & Thyroid Surgery)
Breast cancer is the abnormal growth of cancer cells in the breast. These cancerous cells can grow over time and potentially spread to other parts of your body.
According to the Singapore Cancer Society, breast cancer is the most common cancer among Singaporean women, with around 1,000 women diagnosed annually. Furthermore, approximately 1 in 13 Singaporean women will be diagnosed with breast cancer throughout their lifetime.
The common symptoms of breast cancer may include:
Breast cancer screening is crucial as it allows doctors to diagnose breast cancer in patients at an early stage, hence enabling simpler treatments and better survival.
Breast cancer usually begins as a precancerous lesion and eventually develops into invasive cancer. It usually begins with changes within the breast that are often not noticeable by the patient. It can be changes that are as small and fine as grains of sands. However, breast screening with scans can detect these changes and enable early diagnosis and treatment of these early breast cancer lesions. Usually, when these lesions are so small, the treatment for breast cancer is much simpler and there is a better chance of survival. Because, breast cancer is not an uncommon disease, hence all women should undergo regular breast screening.
Breast cancer screening as early detection of cancer cells can increase your survival rate with early treatment.
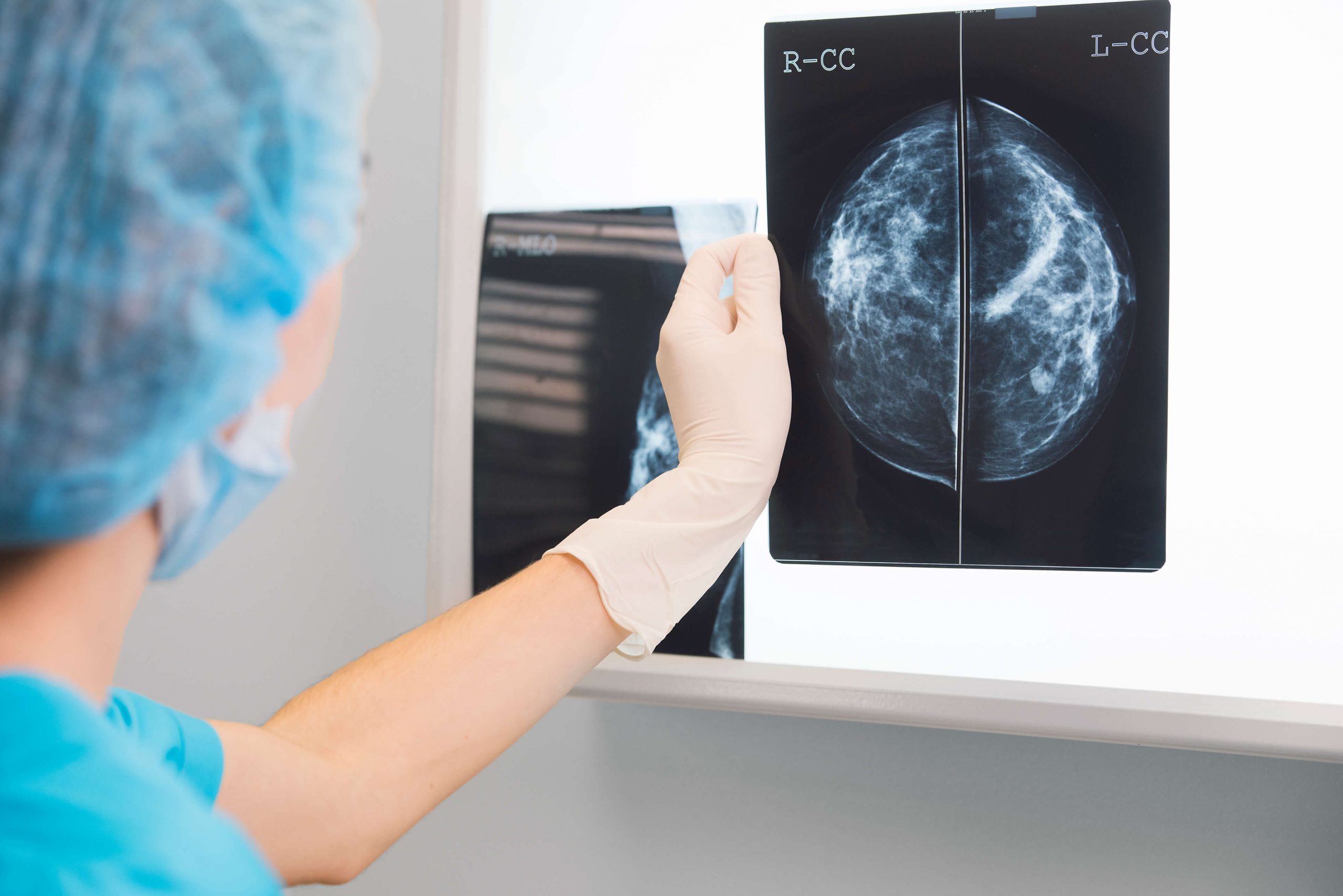
Mammography is an imaging test to examine and detect abnormalities in the breast area using x-rays. It is one of the most common and reliable methods for detecting early breast cancer as it allows the detection of cancerous tumours or lumps that are not large enough to be felt or noticed.
The advantages of mammography include:
Similar to most screening methods, there are also risks involved during mammography.
During mammography, your breasts are exposed to a small amount of radiation. As such, there is a risk of radiation due to x-ray procedure. However, as the radiation emitted is of low dosage, there is generally no significant harm to your body.
There is also a possibility of false-positive results, hence, the possibility of over-treatment. For patients with dense breasts, there is an increased risk of false-negative results from the screening mammography, as both the dense breast and cancers may appear white on regular mammography. Unfortunately, we now know that increased breast density is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. Hence, it is important to discuss this with your Breast Specialist to overcome this via alternate methods of screening, based on your individual risk.
Both 2D and 3D mammograms are largely similar as they use a low-dose x-ray machine to examine the breast area. However, there are still slight differences between them, such as how the images are taken and the manner the results are presented.
A 2D mammogram takes two pictures of each breast to create two images of each breast.
A 3D mammogram takes multiple images of each breast from different angles and shows individual layers of breast tissue. These images are then constructed together to present a 3D view of the breasts. As such, finer details of the breast can be viewed clearly, significantly reducing unnecessary recall and false-negative test results.
During a mammogram, the x-ray technician will gently compress both your breasts between two transparent plates. Images of each breast will then be taken from different angles (depending on whether you are doing a 2D or 3D mammogram) by special x-ray equipment.
There are generally two types of mammograms, digital and non-digital (film-screen). Both mammograms operate the same way, with the digital method preferred as it can minimise background noise, resulting in clearer images of the breast.
Apart from mammograms, there are also many other additional screening options available. A mammogram is usually sufficient to detect breast cancer. However, there may be instances where further tests may be required in certain scenarios.
These alternative screening options include:
According to Singapore national screening guidelines, normal-risk Singaporean women aged 40 and above are recommended to go for a mammogram screening once every year. For those aged 50 and above, a mammogram screening is recommended once every 2 years.
Women in high-risk groups, such as those with a family history of breast cancer or other types of cancer, should see a Breast cancer specialist to discuss their individual risk and may have to commence screening earlier.
You should consult your doctor or breast specialist to discuss your individual risk of breast cancer and the benefits and risks of the various screening options or if you suspect you may have breast cancer due to the detection of abnormalities in your breast.
Breast cancer may be the most common cancer among Singaporean women, but it is treatable if detected early. Early detection through the various screening options is the key to improving the chances of surviving breast cancer.
Contact Dr. Tan Chuan Chien to schedule a breast cancer screening today: https://cctansurgery.com.sg/contact-us/


We are equipped with modern and updated equipment, and a team that will take care of all your needs.
Dr. Tan is a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (FRACS). He is also accredited to practice as a Specialist in both Singapore and Australia.
Dr. Tan firmly believes that transdisciplinary care is the key to every patient’s recovery journey.
Dr Tan is available via video-consultations for patients who are not in Singapore.


Dr. Tan Chuan Chien is a Fellowship-trained Breast and Endocrine Surgeon practicing as a Consultant General Surgeon at Gleneagles Hospital, Singapore. He also sees patients at Mount Elizabeth Novena Specialist Centre and Parkway East Medical Centre. Dr. Tan is a registered Specialist Surgeon (General Surgery) in both Singapore and Australia.
Please fill up this form and we’ll get back to you shortly!
